The Alarming Surge of Hizb ut-Tahrir in Bangladesh
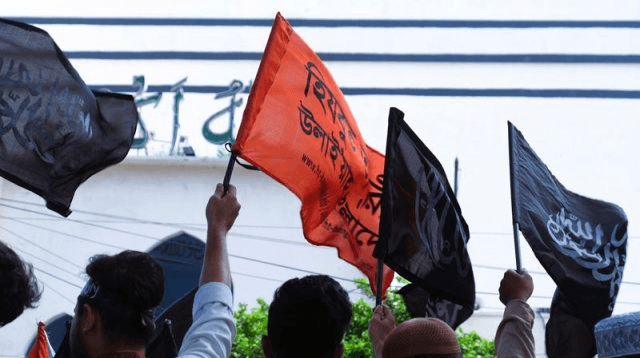
The situation with Hizb ut-Tahrir (HuT) in Bangladesh and its implications for South Asia present complex security and geopolitical challenges. The Indian government banned Hizb ut-Tahrir (HuT) on October 10, 2024, under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, citing the organization’s threats to national security and its aim to establish an Islamic state and caliphate through jihad and terrorist activities.
Recent Activities of Hizb ut-Tahrir in Bangladesh
Public Demonstrations and Symbolism
There have been reports of students from prestigious institutions in Dhaka marching with black flags reminiscent of ISIS, demanding the establishment of a caliphate. This indicates a bold assertion of HuT’s ideology in public spaces, suggesting a level of confidence or support that allows such demonstrations.
Recruitment and Radicalization
HuT has successfully penetrated educational institutions, targeting the educated youth. This recruitment strategy focuses on dissatisfaction with current political and social conditions, offering an Islamist solution that appeals to a segment disillusioned with secular governance.
Government Stance
Despite being banned in Bangladesh since 2009, HuT’s activities suggest that the ban has not fully curtailed its operations. The group’s persistence indicates a lack of enforcement or HuT’s ability to operate covertly or under different guises.
Implications for India
Security Concerns
The rise of HuT next door could lead to radicalization spillover into India, especially in states with significant Muslim populations or those near the Bangladesh border. This could manifest as increased support for extremist ideologies, potential for lone wolf attacks, or even organized terrorist activities.
Cross-Border Terrorism
With a porous border, there’s a heightened risk of militants crossing over for operations in India. This isn’t just theoretical; historical precedents exist where militant outfits have used Bangladesh as a route.
Ideological Influence
The ideological underpinnings of groups like HuT, which promote a global caliphate, directly challenge India’s secular and democratic principles. If this ideology gains traction, it could exacerbate communal tensions within India, potentially leading to social unrest or conflict.
Indian Government’s Response
India’s decision to ban HuT reflects an attempt to pre-emptively address the threat of radical Islamist ideologies gaining ground. However, the effectiveness of such bans often relies on proactive intelligence, community engagement, and robust counter-radicalization strategies.
Broader Regional Security
Alliances with Other Groups: There’s mention of collaboration or at least ideological alignment between HuT and other Islamist entities like Jamaat-e-Islami, suggesting a broader Islamist movement in Bangladesh, which could have ripple effects across South Asia.
Cultural and Political Impact: The targeting of religious minorities, as noted with attacks against Hindus, indicates an effort to impose religious homogeneity, which could destabilize Bangladesh’s secular fabric. This has implications for India, where radical elements could employ similar tactics.
The rise of Hizb ut-Tahrir in Bangladesh and its ideological reach pose multifaceted challenges for India. It requires a security response, diplomatic engagement with Bangladesh, regional cooperation, and internal measures to counter radical narratives. India’s move to ban HuT is a step in acknowledging this threat. Still, the broader strategy must include measures to address the root causes of radicalization, strengthen border controls, and enhance intelligence sharing. The situation underscores the need for continuous vigilance and adaptive security policies in the face of evolving Islamist extremism.








